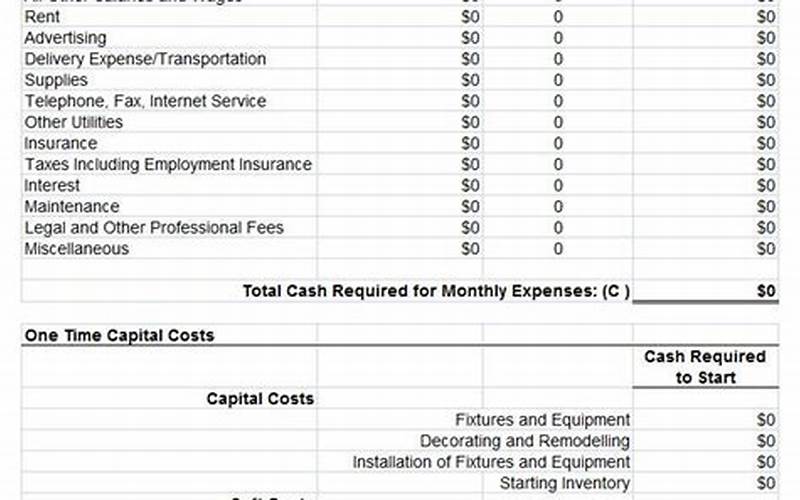
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding the start-up costs for a business. Whether you are a budding entrepreneur or an aspiring business owner, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the financial investment required to launch your venture successfully. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of start-up costs, helping you navigate through the potential expenses and make informed decisions. So, let’s dive in and demystify the world of business start-up costs!
Contents
- 1 Understanding Start-up Costs
- 2 Differentiating Fixed and Variable Costs
- 3 Identifying Essential Start-up Expenses
- 4 Budgeting for Legal and Regulatory Costs
- 5 Calculating Marketing and Advertising Expenses
- 6 Estimating Technology and Equipment Costs
- 7 Determining Staffing and Payroll Expenses
- 8 Accounting for Overhead and Administrative Costs
- 9 Considering Contingency Funds
- 10 Seeking Funding Options
Understanding Start-up Costs
Before embarking on your entrepreneurial journey, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what start-up costs entail. Start-up costs refer to the expenses incurred when setting up a new business. These costs are crucial to consider as they directly impact your initial investment and financial planning.
Initial Investments: One component of start-up costs includes the initial investments required to get your business off the ground. This can involve purchasing or leasing property, acquiring necessary equipment, and even securing intellectual property rights.
- Unveiling the Essentials: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Start-Up Definition
- Revolutionizing Traditional Industries: Unveiling Powerful Digital Transformation Strategies
- Exploring Lucrative Business Ideas: Unveiling Untapped Opportunities for Aspiring Entrepreneurs
- Top 10 Profitable Small Business Ideas to Kickstart in 2023
- Mastering Organizational Agility: Navigating Market Shifts with Ease
Legal and Administrative Fees: Another factor contributing to start-up costs involves legal and administrative fees. These expenses can include business registration, licensing, permits, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It’s essential to allocate a portion of your budget for these expenses to ensure your business operates within the legal framework.
Market Research and Feasibility Studies: Conducting market research and feasibility studies is crucial for understanding your target audience, competition, and market trends. While it may not be a direct monetary expense, the time and resources invested in these activities should be considered as part of your start-up costs.
Product Development and Prototyping: If you’re launching a product-based business, costs associated with product development and prototyping must be factored in. This can include research and development, design, manufacturing, and testing. Properly budgeting for these expenses ensures the quality and functionality of your product.
Branding and Marketing: Building brand awareness and promoting your business is essential for attracting customers. Branding and marketing expenses can include logo design, website development, advertising campaigns, and promotional materials. Allocating funds for these activities is crucial for creating a strong market presence.
Initial Inventory and Supplies: Depending on your business type, you may need to invest in initial inventory and supplies. This includes stocking up on products or raw materials necessary for your operations. Accurately estimating these costs is vital to ensure a smooth start for your business.
By understanding the various components of start-up costs, you can create a comprehensive budget that covers all necessary expenses. Proper financial planning and allocation of resources will set your business on the right track from the beginning.
Differentiating Fixed and Variable Costs
When considering start-up costs for your business, it’s important to differentiate between fixed and variable costs. Understanding these distinctions will help you make informed decisions and effectively manage your finances.
Fixed Costs:
Rent and Utilities: Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of your business’s performance. These include monthly rent for your office or retail space, as well as utilities such as electricity, water, and internet services. It’s important to accurately estimate these costs and include them in your budget from the start.
Insurance: Another fixed cost to consider is insurance. Depending on your business type and industry, you may need various insurance policies to protect your assets, employees, and customers. These can include general liability insurance, professional liability insurance, property insurance, and workers’ compensation insurance.
Salaries and Benefits: If you plan on hiring employees, their salaries and benefits are fixed costs that need to be accounted for. This includes wages, health insurance, retirement plans, and any other employee benefits you may offer. Properly budgeting for these costs ensures that you can attract and retain the right talent for your business.
Variable Costs:
Raw Materials: Variable costs are expenses that fluctuate based on your business’s production or sales volume. For example, if you operate a manufacturing business, the cost of raw materials will vary depending on how much you produce. It’s important to monitor and manage these costs closely to maintain profitability.
Inventory: If you’re in the retail or e-commerce industry, inventory costs are a significant variable expense. The cost of purchasing and restocking inventory will vary based on demand and seasonality. Effective inventory management is crucial to avoid overstocking or understocking, which can impact your cash flow and profitability.
Marketing and Advertising: Variable costs also include marketing and advertising expenses. These costs can vary depending on the channels and strategies you employ to promote your business. Whether it’s digital advertising, social media campaigns, or print materials, monitoring the effectiveness of your marketing efforts is essential to optimize your return on investment.
By understanding the distinction between fixed and variable costs, you can make strategic decisions to optimize your business’s financial health. Proper budgeting and monitoring of these costs will contribute to your overall profitability and success.
Identifying Essential Start-up Expenses
When starting a business, there are several essential expenses that you need to identify and account for in your start-up budget. These expenses are necessary to ensure a successful launch and establish a solid foundation for your business. Let’s explore some of the most common essential start-up expenses:
Market Research:
Understanding Your Target Audience: Conducting market research is crucial for identifying and understanding your target audience. This involves analyzing demographics, consumer behavior, and market trends. Market research expenses may include surveys, focus groups, and hiring research firms to gather valuable insights.
Product Development and Prototyping:
Research and Development: If your business involves creating new products, allocating funds for research and development is essential. This includes activities such as designing prototypes, conducting product testing, and making necessary improvements before launching your final product.
Branding and Logo Design:
Creating a Strong Brand Identity: Building a strong brand presence is vital for attracting customers and differentiating yourself from competitors. Expenses related to branding and logo design may include hiring graphic designers, developing a brand style guide, and creating marketing materials that align with your brand identity.
Website Development:
Establishing an Online Presence: In today’s digital age, having a professional website is crucial for businesses of all types. This includes website design and development, purchasing a domain name, and hosting fees. Allocating resources for website development ensures that you have an online platform to showcase your products or services.
Initial Inventory Procurement:
Stocking Up on Inventory: If you’re running a retail or e-commerce business, allocating funds for initial inventory procurement is essential. This involves purchasing products or raw materials that you will sell or use in your operations. Properly estimating your initial inventory needs will help you meet customer demands and fulfill orders efficiently.
By identifying these essential start-up expenses, you can create a comprehensive budget that covers all necessary aspects of launching your business. Effective financial planning and allocation of resources will set a strong foundation for your venture’s success.
Budgeting for Legal and Regulatory Costs
Starting a business involves legal and regulatory processes that often come with associated costs. It’s crucial to budget for these expenses to ensure compliance and protect your business. Here are some key legal and regulatory costs to consider:
Business Registration and Licensing:
Registering Your Business: Depending on your business structure, you may need to register your business with the appropriate government agencies. This includes obtaining a tax identification number and registering your business name. Fees associated with business registration can vary based on your location and business type.
Licensing and Permits: Certain industries require specific licenses and permits to operate legally. This can include professional licenses, health and safety permits, alcohol licenses, and more. Research the requirements for your industry and allocate funds for obtaining the necessary licenses and permits.
Intellectual Property Protection:
Trademark Registration: If you have a unique brand name, logo, or slogan, it’s essential to protect your intellectual property through trademark registration. This involves conducting a thorough search, filing the necessary applications, and paying registration fees. Budgeting for trademark registration ensures the protection of your brand identity.
Patents and Copyrights: Depending on your business’s nature, you may also need to consider the costs associated with obtaining patents or copyrights for your inventions, designs, or creative works. These legal protections safeguard your intellectual property from infringement.
Compliance with Industry Regulations:
Industry-Specific Regulations: Depending on your industry, there may be specific regulations and compliance requirements that you need to adhere to. This can include health and safety regulations, environmental regulations, data protection laws, and more. Allocate funds for any necessary inspections, certifications, or ongoing compliance measures.
Legal Advice and Contracts: It’s wise to seek legal advice when starting a business to ensure that your contracts, agreements, and other legal documents are properly drafted and protect your interests. Budget for the costs of legal consultations, contract reviews, and any ongoing legal support that may be required.
By budgeting for legal and regulatory costs, you can avoid potential legal issues, penalties, or delays in your business operations. It’s crucial to consult with legal professionals to understand the specific requirements and costs associated with your business and industry.
Calculating Marketing and Advertising Expenses
Marketing and advertising play a vital role in attracting customers and promoting your business. Allocating a portion of your start-up budget for marketing expenses is essential to create brand awareness and drive sales. Here are some key factors to consider when calculating your marketing and advertising expenses:
Marketing Strategy and Planning:
Developing a Marketing Plan: A well-defined marketing plan is crucial for guiding your marketing efforts. This includes identifying your target audience, defining your unique selling proposition, and determining the most effective marketing channels for your business. Consider the costs associated with market research, competitor analysis, and developing a comprehensive marketing strategy.
Website and Online Presence:
Website Design and Development: In today’s digital landscape, having a professional website is essential. Budget for website design, development, and maintenance costs. This includes creating engaging content, optimizing for search engines, and ensuring mobile responsiveness.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): SEO is crucial for improving your website’s visibility in search engine results. Consider the costs of keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, and ongoing SEO efforts to drive organic traffic to your website.
Digital Advertising:
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: PPC advertising allows you to display ads on search engines or social media platforms and pay only when someone clicks on your ad. Budget for keyword research, ad creation, and ongoing campaign management costs.
Social Media Advertising: Social media platforms offer targeted advertising options to reach your specific audience. Consider the costs of creating and promoting ads on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or LinkedIn.
Traditional Advertising:
Print and Broadcast Advertising: If your target audience can be effectively reached through traditional media channels, consider the costs of print ads, radio spots, or television commercials. Keep in mind production costs, media buying, and ongoing campaign management expenses.
Content Marketing:
Content Creation and Distribution: Creating valuable content, such as blog posts, videos, or infographics, can attract and engage your target audience. Budget for content creation, content promotion, and any outsourcing or tools required for content management.
It’s important to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing efforts and make adjustments as needed. Monitoring and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) will help you optimize your marketing budget and maximize your return on investment.
Estimating Technology and Equipment Costs
Depending on your business type and industry, you may need to invest in various technologies and equipment to support your operations. Estimating these costs accurately is crucial for budgeting and ensuring you have the necessary tools to run your business effectively. Here are some key considerations when estimating technology and equipment costs:
Computers and Software:
Hardware: Consider the number of computers or laptops you’ll need for your team. Estimate the costs of purchasing or leasing these devices, along with necessary peripherals such as monitors, keyboards, and printers.
Software: Identify the software applications required for your business operations. This can include productivity software, accounting software, project management tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and industry-specific software. Research the costs of purchasing licenses or subscribing to software services.
Production Equipment:
Machinery and Tools: If your business involves manufacturing or production, estimate the costs of machinery, tools, or equipment needed for your production processes. Consider both initial purchase or lease costs and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Specialized Equipment: Some businesses may require specialized equipment or tools specific to their industry. This can include medical equipment, restaurant kitchen equipment, construction machinery, or scientific instruments. Research the costs associated with acquiring or leasing this specialized equipment.
Communication and Networking:
Internet and Networking: Estimate the costs of setting up internet connectivity, routers, switches, and other networking equipment required for your business’s communication needs. Consider both the initial setup costs and ongoing monthly fees.
Phone Systems: Depending on your communication requirements, budget for the costs of setting up a business phone system. This can include traditional landline systems, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems, or mobile plans for your employees.
Security Systems:
Physical Security: If your business has physical premises, consider the costs of security systems such as surveillance cameras, alarm systems, access control systems, and security personnel if needed.
Digital Security: Protecting your business from cyber threats is essential. Estimate the costs of antivirus software, firewalls, data backup systems, and any cybersecurity services or consultants required.
By accurately estimating technology and equipment costs, you can ensure that you have the necessary tools and infrastructure to support your business operations. It’s important to research prices, consider both upfront and ongoing expenses, and prioritize investments based on your business’s needs.
Determining Staffing and Payroll Expenses
Depending on the nature and scale of your business, you may need to hire employees to support your operations. Understanding and budgeting for staffing and payroll expenses is crucial for building a capable team and ensuring their compensation is in line with industry standards. Here are some key factors to consider when determining staffing and payroll expenses:
Employee Salaries and Wages:
Salary Structure: Research industry salary benchmarks to determine competitive salary ranges for different positions within your business. Consider factors such as experience, qualifications, and job responsibilities when setting salary levels.
Hourly Wages: If you have hourly employees, determine the appropriate wage rates based on local minimum wage laws and prevailing rates in your industry. Consider any overtime pay requirements as well.
Employee Benefits:
Health Insurance: If you plan to offer health insurance benefits to your employees, estimate the costs of premiums, deductibles, and other expenses associated with providing health coverage. Research insurance providers and obtain quotes to determine the most suitable options for your business.
Retirement Plans: Consider whether you will offer retirement plans such as 401(k) or Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and budget for any employer contributions or matching programs you plan to provide.
Paid Time Off: Determine the amount of paid time off (PTO) you plan to offer employees, including vacation days, sick leave, and holidays. Consider any legal requirements and industry norms when calculating the associated costs.
Training and Development:
Onboarding and Training: Budget for the costs of onboarding new employees, including training materials, software licenses, and any external training programs or workshops. Ongoing professional development opportunities should also be considered in your budget.
Outsourcing and Contractors:
Contractors and Freelancers: Depending on your business model, you may need to hire contractors or freelancers for specific projects or tasks. Estimate the costs associated with engaging external resources and factor them into your staffing budget.
Professional Services: If you require specialized services for legal, accounting, or other professional needs, budget for the costs of hiring external professionals or firms to provide these services on an as-needed basis.
Properly assessing your staffing and payroll expenses ensures that you can attract and retain the right talent and compensate them fairly. It’s important to consider both salary and benefits, as well as any additional costs associated with training, outsourcing, or engaging professional services.
Accounting for Overhead and Administrative Costs
When budgeting for your start-up costs, it’s crucial to account for overhead and administrative expenses. These costs may not be directly tied to the production of goods or services, but they are necessary for the smooth functioning of your business. Here are some key overhead and administrative costs to consider:
Office Rent and Utilities:
Rental Expenses: If you have a physical office space, calculate the monthly rent or lease payments. Consider factors such as location, size, and amenities when budgeting for office space.
Utilities: Estimate the monthly costs of utilities such as electricity, water, heating, and internet services. These expenses are essential for maintaining a functional workplace.
Insurance:
General Liability Insurance: Protecting your business from potential risks and liabilities is crucial. Budget for the costs of general liability insurance, which covers damages or injuries caused by your business operations.
Property Insurance: If you own or lease a physical space, consider property insurance to protect your assets from damages or loss due to theft, fire, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events.
Office Supplies and Equipment:
Stationery and Supplies: Estimate the costs of office supplies such as paper, pens, printer ink, and other consumables required for day-to-day operations.
Equipment Maintenance: If you have office equipment, budget for the costs of regular maintenance and repairs to ensure their smooth functioning.
Professional Services:
Bookkeeping and Accounting: Consider hiring a professional bookkeeper or accountant to manage your financial records, prepare tax returns, and provide financial advice. Budget for the fees associated with these services.
Legal Services: Depending on your business’s needs, you may require legal advice for contracts, agreements, or other legal matters. Estimate the costs of engaging legal services as needed.
Marketing and Advertising Materials:
Printed Materials: If your business requires printed materials such as brochures, business cards, or signage, budget for the costs of design, printing, and distribution.
Online Subscriptions and Tools: Consider any online subscriptions or tools required for administrative tasks, project management, or collaboration. These may include software for accounting, document management, communication, or team collaboration.
By accounting for overhead and administrative costs, you can ensure that your business operates smoothly and efficiently. Proper financial planning and allocation of resources for these essential expenses contribute to the overall success and stability of your start-up.
Considering Contingency Funds
When budgeting for your start-up costs, it’s important to set aside a contingency fund to account for unexpected expenses or emergencies. Having a financial buffer can help you navigate through uncertain times without jeopardizing the sustainability of your business. Here are some key considerations when allocating funds for contingency:
Unforeseen Expenses:
Equipment Breakdown: Equipment can malfunction or break down unexpectedly, requiring repairs or replacements. Budgeting for potential equipment failures ensures that you can address these issues without disrupting your operations.
Legal Issues: Your business may encounter unforeseen legal matters, such as lawsuits or contractual disputes. Allocating funds for legal fees and potential settlements can help you handle these situations effectively.
Market Fluctuations:
Economic Downturns: During economic downturns or recessions, businesses may experience a decline in sales or revenue. Having a contingency fund allows you to navigate through challenging times and maintain your business’s stability.
Changes in Market Conditions: Market conditions can change rapidly, impacting your business’s profitability and viability. Having funds set aside can help you adapt to market shifts, invest in new strategies, or explore alternative revenue streams.
Opportunities for Growth:
New Opportunities: Unexpected opportunities may arise that require additional investment. Whether it’s acquiring a competitor, expanding into a new market, or launching a new product, having a contingency fund allows you to seize these opportunities without straining your finances.
Emergency Situations:
Natural Disasters: Natural disasters or unforeseen events can disrupt your business operations. Having a contingency fund can help you recover and resume your operations more quickly.
Health Emergencies: Personal emergencies or health issues can impact your ability to run your business. Having funds set aside can provide some financial security during challenging personal times.
By setting aside a contingency fund, you can protect your business from unexpected expenses or emergencies. It’s important to regularly review and replenish this fund to ensure its adequacy and adjust it as your business grows and evolves.
Seeking Funding Options
If your start-up costs exceed your available resources, exploring funding options can be crucial. Obtaining additional funding can provide the necessary capital to launch and grow your business. Here are some funding options to consider:
Small Business Loans:
Bank Loans: Traditional bank loans are a common option for financing start-up costs. Research different banks and financial institutions to find loan options that suit your business needs. Prepare a comprehensive business plan and financial projections to increase your chances of securing a loan.
Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans: The U.S. Small Business Administration offers various loan programs specifically designed for small businesses. These loans often come with favorable terms and lower interest rates. Explore SBA loan options and eligibility requirements.
Investors and Venture Capital:
Angel Investors: Angel investors are individuals who provide capital in exchange for equity in your business. They often specialize in specific industries and can provide expertise and mentorship along with funding.
Venture Capital: Venture capital firms invest in high-growth potential businesses. They typically provide larger amounts of capital in exchange for equity and often seek an exit strategy, such as an initial public offering (IPO) or acquisition, to generate returns on their investments.
Crowdfunding:
Rewards-Based Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo allow you to raise funds by offering rewards or pre-selling your products or services to backers. Create an engaging campaign and promote it to attract supporters.
Equity-Based Crowdfunding: Equity crowdfunding platforms enable you to raise funds by selling shares of your business to a large number of investors. Research different platforms and comply with the regulations and disclosure requirements for equity crowdfunding.
Grants and Competitions:
Government Grants: Governments, both at the national and local levels, may offer grants to support small businesses. Research grant opportunities relevant to your industry and location.
Business Competitions: Participating in business competitions can provide funding and exposure for your start-up. Look for competitions that align with your business model or industry and prepare a compelling pitch to increase your chances of winning.
When seeking funding, it’s important to thoroughly research and understand the terms, requirements, and potential implications of each option. Prepare a solid business plan, financial projections, and a compelling pitch to increase your chances of securing funding for your start-up.
In conclusion, understanding and budgeting for start-up costs is essential for launching a successful business. By carefully considering and estimating the various expenses involved, you can create a comprehensive budget that covers all necessary aspects. From start-up investments and legal fees to marketing expenses and staffing costs, each component contributes to the overall financial health of your venture.
Remember to differentiate between fixed and variable costs, as well as identify essential start-up expenses specific to your industry. Additionally, accounting for overhead and administrative costs, setting aside contingency funds, and exploring funding options can provide stability and flexibility for your business.
Throughout your entrepreneurial journey, it’s crucial to regularly review and adjust your budget as circumstances evolve. Stay proactive in monitoring your financial performance, seeking opportunities for cost optimization, and adapting your strategies as necessary.
By approaching start-up costs with careful planning and a realistic outlook, you can set your business on the path to success. Remember, a well-executed financial plan is not only crucial for launching your venture but also for sustaining and growing it in the long run.

