As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, workplace automation has become an increasingly prevalent topic of discussion. From intelligent algorithms to robotic process automation, businesses are adopting various forms of automation to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. However, this shift towards automation raises questions about the impact it will have on job roles and the skills required in the workforce. In this article, we will explore the evolving landscape of workplace automation and delve into the implications it has on job roles and the acquisition of new skills.
Contents
- 1 1. Introduction: Understanding Workplace Automation
- 2 2. Types of Workplace Automation
- 3 3. Benefits of Workplace Automation
- 4 4. Impact on Job Roles
- 5 5. Adaptation and Reskilling Opportunities
- 6 6. Collaboration between Humans and Machines
- 7 7. Ethical Considerations of Workplace Automation
- 8 8. Industries Embracing Automation
- 9 9. Challenges in Implementing Automation
- 10 10. Future Outlook: The Role of Automation in the Workplace
1. Introduction: Understanding Workplace Automation
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, workplace automation has become a prominent topic of discussion. As organizations strive to streamline their operations and improve efficiency, they are increasingly turning to automation technologies. From intelligent algorithms to robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI), automation is reshaping the way we work.
Workplace automation refers to the use of technology to automate repetitive tasks and processes that were previously performed by humans. It involves the integration of various technologies and software systems to perform these tasks efficiently and accurately. The goal of automation is to free up human resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- The Ultimate Guide: 10 Easiest Business Ideas to Kickstart Your Entrepreneurial Journey
- Exploring Lucrative Business Ideas: Unveiling Untapped Opportunities for Aspiring Entrepreneurs
- Mastering Competitive Market Pricing: Unleashing the Power of Value-Based and Dynamic Strategies
- Building Resilient Strategies: Ensuring Just-in-Time Manufacturing with Robust Supply Chains
- Unveiling Lucrative Business Ideas: Your Ultimate Guide to Starting a Successful Venture in the UK
The Significance of Workplace Automation
Automation offers several significant advantages for businesses. Firstly, it enhances productivity by reducing manual errors and eliminating time-consuming tasks. With automation, repetitive processes can be completed faster and with greater accuracy, resulting in increased output and efficiency.
Furthermore, automation enables organizations to improve their operational agility and responsiveness. By automating routine tasks, businesses can be more flexible in adapting to changing market demands and customer needs. This agility allows companies to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
The Role of Technology in Workplace Automation
Various technologies drive workplace automation. Robotic process automation (RPA) involves the use of software robots to mimic human actions and perform repetitive tasks. These robots can interact with different applications, extract data, and perform rule-based tasks, freeing employees from mundane activities.
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in automation as well. AI-powered systems can learn from data, make intelligent decisions, and automate complex processes. Machine learning algorithms enable systems to improve their performance over time by analyzing patterns and adapting to changing circumstances.
Additionally, the Internet of Things (IoT) enables the connection of physical devices and sensors, allowing for data collection and automation of processes in various industries. This interconnectedness enables machines to communicate and collaborate, leading to enhanced efficiency and productivity.
In the following sections, we will explore the different types of workplace automation, the benefits it offers, and the impact it has on job roles and skills. We will also address the challenges and ethical considerations associated with automation, as well as provide insights into industries already embracing automation. Finally, we will discuss the future outlook for workplace automation and its implications on the workforce.
2. Types of Workplace Automation
Workplace automation encompasses a wide range of technologies that can streamline and optimize various business processes. Understanding the different types of automation is crucial in grasping the potential impact on job roles and skills required in the workforce.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation involves the use of software robots or “bots” to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks. These bots can mimic human actions by interacting with user interfaces, extracting data, and executing processes across different applications. RPA is particularly effective in automating tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Automation
Artificial Intelligence automation leverages advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities to automate complex tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, learn from patterns, and make intelligent decisions. Natural Language Processing (NLP) and computer vision are examples of AI technologies that automate tasks like customer support chatbots and image recognition.
Intelligent Workflow Automation
Intelligent Workflow Automation combines RPA with AI to automate end-to-end business processes. It involves the integration of various systems and applications to streamline workflows, eliminate manual handoffs, and ensure seamless information flow across departments. Intelligent Workflow Automation can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce errors in processes like purchase order approvals, employee onboarding, and supply chain management.
Cognitive Automation
Cognitive Automation focuses on replicating human cognitive abilities through technology. This form of automation involves systems that can understand, interpret, and respond to unstructured data, such as text and images. Cognitive automation technologies enable tasks like sentiment analysis, content categorization, and data extraction from documents, enhancing efficiency in industries like finance, legal, and healthcare.
Physical Robotics
Physical robotics refers to the use of robotic systems to perform physical tasks in industrial or service environments. These robots can be programmed to handle repetitive and physically demanding tasks, such as assembly line operations, packaging, and even customer assistance in retail. Physical robotics not only improves efficiency but also enhances workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Understanding these different types of workplace automation provides a foundation for comprehending how job roles may evolve and the skills that will be in demand in an automated workforce. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits of workplace automation, the impact on job roles, and the opportunities for employees to adapt and acquire new skills.
3. Benefits of Workplace Automation
Workplace automation offers numerous benefits for businesses across industries. By streamlining processes and optimizing efficiency, automation can transform how organizations operate and ultimately drive success.
Increased Productivity
One of the primary benefits of automation is the significant increase in productivity it brings. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, employees can focus on more value-added activities that require critical thinking and creativity. This leads to higher output and faster turnaround times, ultimately boosting overall productivity within the organization.
Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automation eliminates the risk of human errors that can occur during manual data entry or repetitive tasks. With the precision and consistency provided by automation technologies, organizations can ensure a higher level of accuracy in their processes. This, in turn, reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes and the need for rework, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
By automating workflows and eliminating manual handoffs, organizations can achieve a higher level of operational efficiency. Automation enables seamless information flow across departments, reducing bottlenecks and delays. This allows for faster decision-making, improved collaboration, and better resource allocation, ultimately driving overall efficiency within the organization.
Cost Savings
Automation can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By reducing the need for manual labor and streamlining processes, organizations can achieve higher productivity levels with fewer resources. Additionally, automation reduces the risk of errors and rework, saving both time and money. Over time, these cost savings can have a substantial impact on the organization’s bottom line.
Improved Customer Experience
Automation can greatly enhance the customer experience by enabling faster response times and improved accuracy in service delivery. For example, automated customer service chatbots can provide instant support, personalized recommendations, and 24/7 availability. By automating certain aspects of customer interactions, organizations can provide a more efficient and satisfying experience, leading to increased customer loyalty and retention.
Adaptability and Scalability
Automation technologies offer adaptability and scalability, allowing organizations to quickly adjust to changing business needs and scale their operations. As processes become more efficient and streamlined through automation, businesses can easily accommodate increased demand or adapt to market fluctuations. This flexibility enables organizations to stay agile and competitive in dynamic business environments.
The benefits of workplace automation are wide-ranging and can have a profound impact on the success and growth of businesses. In the next sections, we will explore the impact of automation on job roles and the skills required in the workforce. We will also discuss the opportunities for employees to adapt and upskill in response to workplace automation.
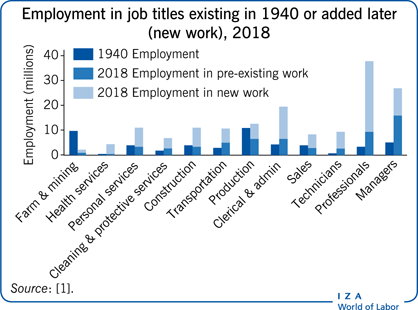
4. Impact on Job Roles
The rise of workplace automation has a profound impact on job roles and the skills required in the workforce. As technology advances and automation becomes more prevalent, certain tasks and responsibilities traditionally performed by humans are being automated.
Task Automation and Job Redefinition
Automation primarily targets repetitive and rule-based tasks that can be easily programmed and executed by machines. This automation can lead to a redefinition of job roles, as employees no longer need to focus on these mundane tasks. Instead, their roles can evolve to include more complex and strategic responsibilities that require human creativity and problem-solving abilities.
Shift in Skill Requirements
The adoption of automation technologies often necessitates a shift in the skills required for various job roles. While some technical skills may become less relevant, new skills come to the forefront. For example, there is an increasing demand for skills such as data analysis, critical thinking, complex problem-solving, and creativity. These skills enable employees to collaborate with automation technologies and leverage their capabilities to achieve optimal results.
Upskilling and Reskilling Opportunities
Automation presents opportunities for employees to upskill and reskill to remain relevant in an automated workforce. By acquiring new skills, individuals can adapt to the changing demands of their job roles and take advantage of the collaborative nature of automation technologies. Organizations can provide training programs, mentorship opportunities, and resources to support employees in this process, ensuring a smooth transition and a skilled workforce.
Job Displacement and New Job Creation
While automation may lead to the displacement of certain job roles, it also creates new job opportunities. As technology takes over repetitive tasks, employees can focus on higher-value work that machines cannot perform. Additionally, the implementation and maintenance of automation technologies require skilled professionals. This shift in job roles can lead to a restructuring of the workforce, with individuals taking on new positions that align with their expanded skill sets.
Collaboration between Humans and Machines
Automation is not meant to replace humans; rather, it aims to augment and enhance human capabilities. Collaboration between humans and machines becomes crucial in an automated workplace. By leveraging automation technologies, employees can work alongside intelligent systems to achieve better outcomes. This collaboration allows for the application of human judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence, complementing the efficiency and precision of automation.
Understanding the impact of workplace automation on job roles is essential for both employees and organizations. In the following sections, we will delve into the opportunities for employees to adapt and acquire new skills to thrive in an automated workforce. We will also address the challenges and ethical considerations associated with automation, as well as provide insights into industries already embracing automation.
5. Adaptation and Reskilling Opportunities
The advent of workplace automation brings forth new opportunities for employees to adapt and acquire new skills in order to thrive in an automated workforce. As job roles evolve and tasks are automated, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their capabilities and remain valuable contributors in their organizations.
Lifelong Learning and Continuous Adaptation
In an automated world, the importance of lifelong learning cannot be overstated. Individuals must embrace a mindset of continuous adaptation and be open to acquiring new skills throughout their careers. This involves staying updated with the latest automation technologies, industry trends, and best practices. By proactively seeking knowledge and learning opportunities, employees can position themselves for success in the automated workplace.
Identifying Transferable Skills
As job roles change due to automation, it is crucial for employees to identify their transferable skills. Transferable skills are those that can be applied across different roles or industries. These skills may include critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, leadership, and adaptability. By recognizing their transferable skills, individuals can leverage them to transition into new roles or industries that align with the changing demands of the job market.
Acquiring Technical Skills
With the increasing prevalence of automation technologies, acquiring technical skills relevant to the automated workplace becomes essential. This may involve learning programming languages, data analysis tools, or specific automation software. By gaining proficiency in these technical skills, individuals can collaborate effectively with automation technologies and harness their power to streamline processes and drive innovation.
Embracing Creativity and Emotional Intelligence
Automation may excel at repetitive and analytical tasks, but it often falls short in areas that require creativity, emotional intelligence, and human interaction. Employees can focus on developing and honing these uniquely human skills. By nurturing creativity, individuals can bring fresh perspectives, innovative ideas, and problem-solving abilities to their work. Furthermore, enhancing emotional intelligence enables employees to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics and build strong relationships with colleagues and clients.
Seeking Opportunities for Upskilling and Reskilling
Organizations play a vital role in supporting employees in their journey of adaptation and reskilling. They can provide opportunities for upskilling and reskilling through training programs, workshops, mentorship, and educational resources. By partnering with employees in their professional development, organizations foster a culture of continuous learning and ensure that their workforce remains equipped with the skills needed to thrive in an automated environment.
Adapting to workplace automation requires a proactive approach from both employees and organizations. In the following sections, we will explore the challenges and ethical considerations associated with automation, as well as provide insights into industries that are already embracing automation. By understanding these factors, individuals and organizations can navigate the automated landscape with confidence and seize the opportunities it presents.
6. Collaboration between Humans and Machines
In an automated workplace, collaboration between humans and machines becomes paramount. Rather than replacing humans, automation technologies are designed to augment human capabilities and enhance productivity. This collaborative approach allows organizations to leverage the strengths of both humans and machines to achieve optimal results.
Enhancing Efficiency and Accuracy
Automation technologies excel at executing repetitive and rule-based tasks with precision and speed. By offloading these tasks to machines, employees can focus on more complex and strategic activities that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This collaboration enhances overall efficiency and accuracy, as humans can dedicate their energy to areas where they can deliver the most value.
Utilizing Human Judgement and Creativity
While machines excel at processing large volumes of data and making data-driven decisions, they lack the ability to exercise human judgement and creativity. Humans possess the capacity to think critically, assess situations holistically, and make nuanced decisions based on their experiences and intuition. By collaborating with machines, employees can leverage their own judgement and creativity to complement the capabilities of automation technologies.
Driving Innovation and Problem-Solving
Collaboration between humans and machines fosters a culture of innovation and problem-solving within organizations. Automation technologies can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns, enabling humans to gain insights and make informed decisions. This collaboration empowers employees to think creatively, explore new possibilities, and leverage automation technologies to drive innovation in their respective fields.
Empowering Employees with Automation Tools
Automation tools and software can empower employees to work more efficiently and effectively. For example, employees can use automation software to automate repetitive administrative tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities. By equipping employees with user-friendly automation tools, organizations enable them to take ownership of their work and leverage automation to their advantage.
Nurturing Human-Centric Skills
Automation technologies cannot replace the human touch and the unique skills that humans bring to the workplace. Organizations should nurture and develop human-centric skills such as empathy, emotional intelligence, and communication. These skills are crucial in building strong relationships with colleagues, clients, and customers, and they enhance the overall collaborative environment in an automated workplace.
Collaboration between humans and machines is the key to unlocking the full potential of workplace automation. By understanding the strengths and limitations of both, organizations can create a harmonious and productive work environment. In the following sections, we will explore the ethical considerations and challenges associated with automation, as well as provide insights into industries that are already embracing automation.
7. Ethical Considerations of Workplace Automation
While workplace automation brings numerous benefits, it also raises important ethical considerations that need to be addressed. As organizations adopt automation technologies, it is crucial to navigate these ethical concerns and ensure that automation is implemented responsibly and in a manner that upholds ethical standards.
Data Privacy and Security
Automation often involves the collection and analysis of large volumes of data. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is of utmost importance. Organizations must implement robust data protection measures, including encryption, access controls, and secure storage. Additionally, transparency about data usage and obtaining informed consent from individuals is essential to maintain trust and ethical standards.
Algorithmic Bias
Automation technologies rely on algorithms to make decisions and predictions. However, these algorithms can be biased, as they are developed based on historical data that may contain inherent biases. Organizations must be vigilant in identifying and addressing algorithmic bias to ensure fair and equitable outcomes. Regular monitoring, testing, and diversifying the data used in algorithm development are crucial steps to mitigate bias and promote ethical decision-making.
Job Displacement and Job Security
The implementation of automation technologies can lead to job displacement, as certain tasks become automated. Organizations should take a proactive approach to address the potential impact on employees and ensure fair transition strategies. This may involve reskilling and upskilling initiatives, providing support for affected employees, and exploring new job opportunities created by automation. Ensuring job security and fostering a culture of lifelong learning are essential for ethical workplace automation.
Ethical Use of Automation Technologies
Organizations must consider the ethical implications of how automation technologies are used. For example, using automation to replace human workers solely for the purpose of reducing costs without considering the societal impact is unethical. Organizations should prioritize the well-being of employees and the broader community when implementing automation, ensuring that it contributes to societal progress and does not perpetuate inequalities.
Human Oversight and Accountability
Automation technologies should be designed with a level of human oversight and accountability. While machines can perform tasks efficiently, human judgment and intervention are still necessary, especially in complex and sensitive situations. Establishing mechanisms for human control and review is important to prevent undue reliance on automation and to ensure that decisions made by automated systems align with ethical values and legal requirements.
Addressing these ethical considerations is crucial for responsible workplace automation. By implementing ethical frameworks, organizations can ensure that automation technologies align with societal values, respect individual rights, and contribute positively to the workforce. In the following sections, we will explore the challenges associated with automation implementation and provide insights into industries that are already embracing automation.
8. Industries Embracing Automation
Automation technologies are being embraced across various industries, transforming the way businesses operate and revolutionizing workflows. Let’s explore some of the industries that have been quick to adopt automation and the benefits they have experienced.
Manufacturing and Assembly
The manufacturing industry has long been at the forefront of automation adoption. Automation technologies such as robotic arms, conveyor systems, and automated assembly lines have significantly improved efficiency and productivity in manufacturing processes. These technologies enable faster production, higher quality control, and reduced labor costs, ultimately leading to increased competitiveness in the global market.
Healthcare and Medicine
Automation is transforming healthcare and medicine, revolutionizing patient care, diagnostics, and research. Robotic surgery systems enhance precision during surgical procedures, while automation tools assist in medication dispensing and laboratory testing. Automation in healthcare improves accuracy, reduces errors, and enhances patient safety. Additionally, automation enables the analysis of large healthcare datasets, leading to more efficient diagnoses, treatment plans, and medical research.
Finance and Banking
The finance and banking industry has embraced automation to streamline processes, enhance customer experiences, and improve efficiency. Automation technologies are used for tasks such as account verification, fraud detection, loan processing, and customer support. These technologies expedite processes, reduce manual errors, and enable faster and more secure transactions. Automation in finance and banking has also led to the development of innovative financial products and services.
Retail and E-commerce
Automation has revolutionized the retail and e-commerce industries, transforming the way products are stocked, distributed, and delivered. Automated inventory management systems ensure accurate stock levels, while robotics assist in order picking and packing. Automation technologies also enable personalized customer experiences through recommendation algorithms and chatbots. By automating repetitive tasks, retail and e-commerce businesses can focus on enhancing customer engagement and delivering seamless shopping experiences.
Customer Service and Support
Automation is reshaping customer service and support functions, improving response times and enhancing customer experiences. Chatbots and virtual agents provide instant support and assistance, answering common queries and directing customers to the right resources. Automation technologies also enable personalized customer interactions by analyzing customer data and preferences. By automating routine customer service tasks, businesses can provide faster and more efficient support, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
These are just a few examples of industries that have embraced automation to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth. As automation technologies continue to advance, more industries are likely to adopt automation to stay competitive and meet the evolving demands of the market. In the following sections, we will explore the challenges associated with automation implementation and provide insights into the future outlook for workplace automation and its impact on the workforce.
9. Challenges in Implementing Automation
While workplace automation offers numerous benefits, organizations may face certain challenges during the implementation process. It is important to be aware of these challenges and develop strategies to overcome them effectively.
Resistance to Change
One of the primary challenges organizations face is resistance to change from employees. Some employees may fear that automation will replace their jobs or disrupt their daily routines. To address this, organizations should communicate openly and transparently about the goals and benefits of automation, involve employees in the process, and provide support and training to help them adapt to new ways of working.
Integration Complexity
Implementing automation technologies often involves integrating various systems and applications. This can be complex, especially when existing infrastructure and legacy systems are involved. Organizations need to carefully plan and execute the integration process, ensuring compatibility and data integrity across different systems. Engaging experienced professionals and leveraging automation consulting services can help mitigate integration challenges.
Cost and Return on Investment
While automation can lead to significant cost savings in the long run, the initial investment costs can be a challenge for organizations. Implementing automation technologies may require upfront investment in hardware, software, training, and infrastructure upgrades. Organizations need to conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to assess the return on investment and make informed decisions regarding automation implementation.
Workforce Transition and Retraining
As automation technologies are adopted, some job roles may evolve or become redundant, requiring workforce transition and retraining. Organizations need to proactively plan for this transition, providing reskilling and upskilling opportunities for employees affected by automation. By investing in employee development and offering support during the transition, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful integration of automation technologies.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Automation raises ethical and legal considerations that organizations must navigate responsibly. Ensuring data privacy, avoiding algorithmic bias, and maintaining compliance with regulations are essential. Organizations should establish ethical frameworks, conduct regular audits, and involve legal experts to address these concerns and ensure that automation is implemented ethically and in accordance with legal requirements.
By anticipating and addressing these challenges, organizations can successfully implement automation technologies and realize the benefits they offer. In the following sections, we will delve into the ethical considerations associated with automation and provide insights into the future outlook for workplace automation and its impact on the workforce.
10. Future Outlook: The Role of Automation in the Workplace
The future of workplace automation is promising, with advancements in technology continuously reshaping the way businesses operate. As automation becomes more prevalent, it is essential to explore the future outlook and anticipate the impact it will have on the workforce.
Emerging Automation Trends
Automation technologies are evolving at a rapid pace, leading to emerging trends that will shape the future of the workplace. These include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into automation systems, the proliferation of robotics in various industries, the increasing use of natural language processing (NLP) for improved human-machine interaction, and the rise of automation-as-a-service platforms that offer accessible and scalable automation solutions.
Advancements in Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation will continue to advance, enabling machines to perform increasingly complex tasks that require cognitive abilities. AI-powered automation systems will become more sophisticated, capable of learning from data, making autonomous decisions, and adapting to dynamic environments. This will lead to improved efficiency, enhanced accuracy, and the ability to automate a wider range of tasks across industries.
The Changing Nature of Job Roles
As automation technologies become more prevalent, job roles will continue to evolve. Repetitive and routine tasks will be automated, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities that require human creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence. Job roles will become more strategic, involving the management and collaboration with automation technologies to achieve business objectives. This shift will require individuals to acquire new skills and adapt to changing job requirements.
Opportunities for Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Automation creates opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship. With the automation of routine tasks, individuals and organizations can explore new avenues for creativity and problem-solving. Automation technologies can enable the development of new products, services, and business models. Entrepreneurs can leverage automation to streamline processes, reduce costs, and bring innovative solutions to the market.
The Importance of Lifelong Learning
As automation technologies evolve, the importance of lifelong learning becomes even more critical. Individuals must embrace a mindset of continuous learning to adapt to the changing demands of the workplace. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will be essential to equip individuals with the necessary skills to thrive in an automated workforce. Organizations should foster a culture of learning, providing resources and opportunities for employees to develop new skills throughout their careers.
The future of workplace automation holds immense potential for innovation, efficiency, and growth. By embracing automation technologies responsibly, organizations can unlock new possibilities and create a workplace that combines the unique strengths of humans and machines. With careful planning, continuous adaptation, and a focus on ethical considerations, the future of work can be shaped into a collaborative and productive environment.
In conclusion, workplace automation is transforming the business landscape, reshaping job roles, and redefining the skills required in the workforce. As organizations adopt automation technologies, they experience increased productivity, improved accuracy, enhanced operational efficiency, and cost savings. However, automation also presents challenges such as resistance to change, integration complexity, and the need for workforce transition and retraining.
Collaboration between humans and machines is key to leveraging the benefits of automation. By combining human judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence with the efficiency and precision of automation technologies, organizations can drive innovation and achieve optimal results. It is crucial to address ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, algorithmic bias, job displacement, and human oversight to ensure that automation is implemented responsibly and ethically.
The future outlook for workplace automation is promising, with emerging trends in AI, ML, robotics, and NLP. Job roles will continue to evolve, requiring individuals to adapt and acquire new skills through lifelong learning. Automation also creates opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship, fostering a culture of creativity and problem-solving.
As we navigate the automated landscape, it is important for organizations to prioritize employee support, providing upskilling and reskilling opportunities to ensure a smooth transition. By embracing automation technologies responsibly and with an ethical mindset, organizations can create a collaborative and productive work environment that leverages the unique strengths of both humans and machines.